What is an IP Address?

An IP address (Internet Protocol) is a unique number assigned to each device connected to a network, whether it's on the Internet or a local network. It's like a postal address for a device on the network, enabling devices to communicate with each other. An IP address consists of a series of numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.0.1. This address uniquely identifies a device and allows it to send and receive data across the network.
Each IP address is divided into two parts: the network part and the host part. The network part identifies the network to which the device belongs, while the host part identifies the specific device within that network. This allows devices to communicate with each other within the same network and also across different networks.
What are Public IPs?

Public IP addresses are those used on the Internet to identify a device and allow it to communicate with other devices on the global network. These addresses are unique and are assigned through Internet Service Providers (ISPs). A public IP address is necessary for a device to access the Internet and receive information from other devices on the network.
When a device connects to the Internet, it is assigned a public IP address by the ISP. This public IP address is visible to other devices on the Internet and allows connections to be established and data to be sent between them. It's like the postal address of a device on the Internet, ensuring that data reaches its destination correctly.
What are Private IPs?
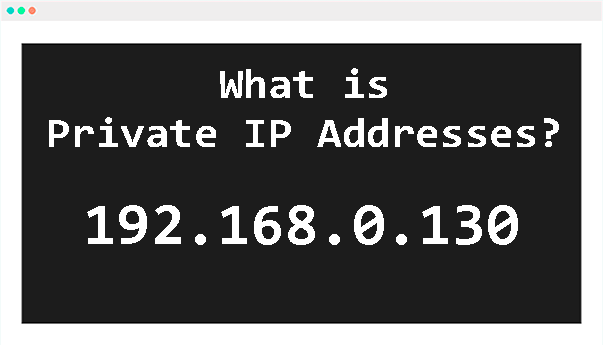
Private IP addresses are used in local networks, such as in a home or office. These addresses are assigned by the network's router and are unique within that specific network. Unlike public IP addresses, private IP addresses are not accessible from the Internet and are used to enable communication between devices within the local network.
Private IP addresses are used to identify and communicate with devices within a local network. For example, in a home network, each connected device, such as computers, smartphones, or printers, will have a unique private IP address assigned by the network's router. This allows devices to communicate with each other and share resources within the local network, such as files or printers.
What are Loopback / Localhost IPs?
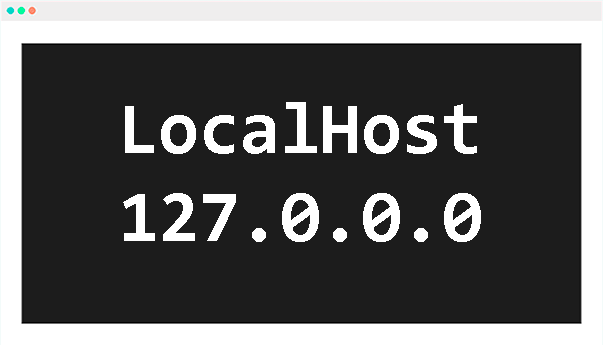
The loopback IP address is a special address used to allow a device to communicate with itself. The most common loopback IP address is 127.0.0.1. When a device sends data to this address, the data is sent back to the same device. This is often used to test applications or services on a device without connecting to an external network.
What are IPv4 and IPv6?

IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) are two versions of the Internet Protocol used to assign IP addresses to devices in a network. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses and is the most widely used version currently.
However, due to the increasing demand for IP addresses, IPv6 has been developed, which uses 128-bit addresses and allows a much larger number of available IP addresses. IPv6 is gradually being implemented to replace IPv4 and ensure there are enough IP addresses for all devices connected to the Internet.